# How is Dew Point Calculated
## Understanding Dew Point
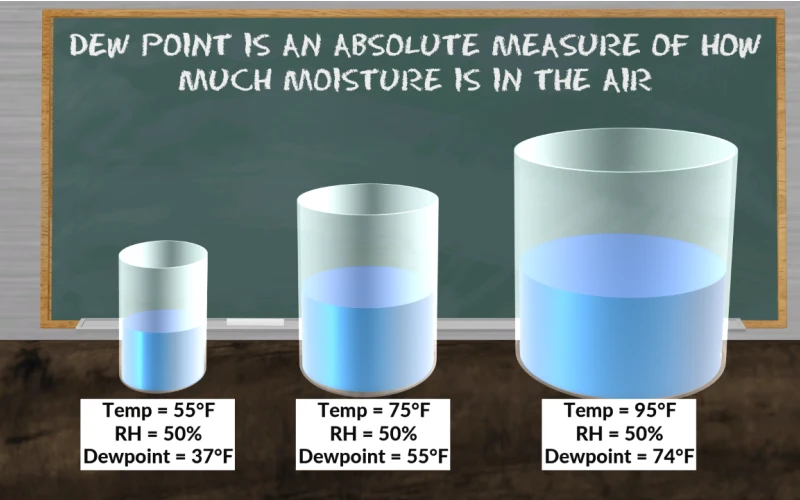
Dew point is the temperature at which air becomes saturated with water vapor, leading to the formation of dew, fog, or frost. It’s a crucial measurement in meteorology, HVAC systems, and various industrial processes. Understanding how dew point is calculated helps predict weather patterns and prevent moisture-related issues in different applications.
## The Science Behind Dew Point Calculation
Calculating dew point involves understanding the relationship between temperature, humidity, and atmospheric pressure. The process relies on several physical principles:
– Water vapor content in air
– Saturation vapor pressure
– Relative humidity
– Temperature variations
## Basic Dew Point Calculation Methods
### 1. Magnus Formula
One of the most common methods for calculating dew point is the Magnus formula:
Td = (b × α(T,RH)) / (a – α(T,RH))
Where:
– Td is the dew point temperature
– T is the air temperature
– RH is the relative humidity
– a and b are constants (a = 17.27, b = 237.7°C)
– α(T,RH) = (a × T)/(b + T) + ln(RH/100)
### 2. Simplified Approximation
For quick estimations, you can use this simplified formula:
Td ≈ T – ((100 – RH)/5)
This approximation works reasonably well when RH is above 50% and temperatures are between 0°C and 60°C.
## Step-by-Step Calculation Process
Let’s walk through a detailed calculation using the Magnus formula:
1. Convert temperature to Celsius if necessary
2. Ensure relative humidity is in percentage form (not decimal)
3. Calculate the intermediate value α(T,RH)
4. Plug values into the Magnus formula
5. Solve for Td (dew point temperature)
## Practical Example
Suppose we have:
– Air temperature (T) = 25°C
– Relative humidity (RH) = 60%
Calculation:
1. α(T,RH) = (17.27 × 25)/(237.7 + 25) + ln(60/100)
2. α(T,RH) ≈ 1.646 + (-0.511) ≈ 1.135
3. Td = (237.7 × 1.135)/(17.27 – 1.135) ≈ 16.7°C
## Factors Affecting Dew Point Accuracy
Several factors can influence the precision of dew point calculations:
– Measurement accuracy of temperature and humidity
– Atmospheric pressure variations
– Presence of contaminants in the air
– Altitude above sea level
## Applications of Dew Point Calculations
Understanding dew point has numerous practical applications:
– Weather forecasting and analysis
– HVAC system design and operation
– Industrial drying processes
– Preventing condensation in buildings
– Agricultural planning
– Aviation safety
## Advanced Calculation Methods
For more precise calculations, especially in industrial settings, professionals might use:
– Psychrometric charts
– Specialized dew point calculators
– Computerized measurement systems
– Empirical data tables
## Conclusion
Dew point calculation is a fundamental process in understanding atmospheric moisture conditions. While the Magnus formula provides a reliable method, various approximations and tools exist for different levels of precision. Whether you’re a meteorologist, HVAC technician, or simply curious about weather patterns, understanding how to calculate dew point offers valuable insights into moisture behavior in our environment.
Keyword: how is dew point calculated